Understanding, Avoiding, and Treating This Common Skin Condition
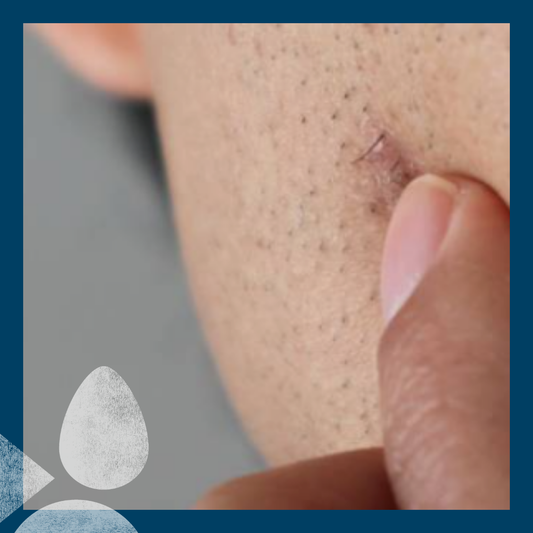
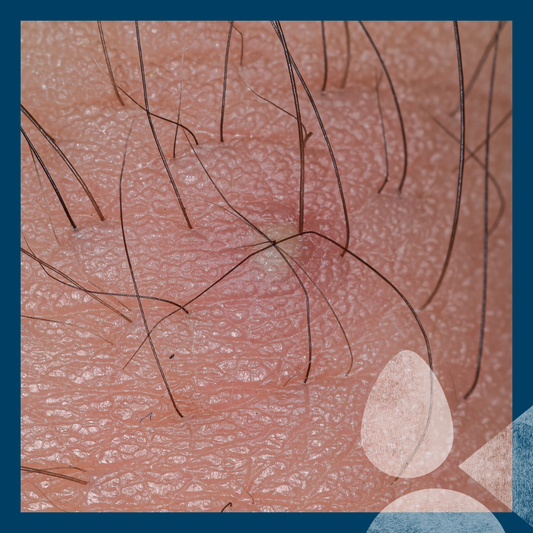
Folliculitis is an inflammation or infection of the hair follicles, and presents as small red or pus-filled bumps around hair follicles. A relatively common skin disorder, folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, such as the scalp, face, back, chest legs, arms/underarms and groin. (In fact the only external parts of your body which are not covered in hair follicles, and therefore where you can’t get folliculitis are your lips, the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet.)
Visible as small, red, and sometimes itchy bumps, folliculitis can cause physical discomfort – such as itching and irritation - as well as looking unsightly. If the inflamed follicles become infected with bacteria or fungi, what starts off spots or rash-type symptoms can progress into pus-filled sores. Though it's usually a superficial skin condition affecting just the upper part of the follicle, severe cases (known as deep folliculitis) can involve the entire hair follicle, leading to potential complications like permanent hair loss or scarring.
Why Do You Get Folliculitis?
Folliculitis often occurs when hair follicles are damaged, allowing for easy entry of bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Hair follicles can become damaged in a variety of ways such as friction from tight clothing, blockage of the follicle (often from sweat, oils, or make-up), injuries to the skin, certain skin conditions like acne or dermatitis, and after some forms/incidents of hair removal. Individuals with compromised immune systems or chronic diseases such as diabetes may be at an increased risk of contracting it.
Folliculitis can also be caught if it’s the variant caused by the contagious bacteria staphylococcus (staph). If you have any open hair follicles, or any cuts or abrasions on your skin, and you do an activity like share a bath, hot tub or towel with someone who has the staph-caused folliculitis, you run the risk of contracting the disorder this way.
How to Avoid Getting Folliculitis
Avoiding folliculitis primarily involves protecting your hair follicles from damage and preventing situations that encourage bacterial or fungal growth. Some practical steps include:
- Avoiding tight clothing that can cause friction on the skin
- Showering immediately after activities that cause sweating, like exercise
- Not sharing personal items such as towels or razors
- Using a clean, sharp razor if shaving and applying a moisturising lotion immediately after shaving
- Keeping skin clean and moisturised on an ongoing basis
How to Prevent Folliculitis
Prevention goes hand in hand with avoidance. In addition to the aforementioned avoidance strategies, maintaining overall good health can also help to prevent folliculitis. This includes:
- Keeping fit and healthy in general – e.g. eating a balanced diet to support a healthy immune system
- Maintaining good hygiene, especially in communal spaces like gyms or swimming pools
- Ensuring any wounds or injuries to the skin are promptly and properly cared for
- Consulting a dermatologist if you have a recurring skin condition or frequent bouts of folliculitis
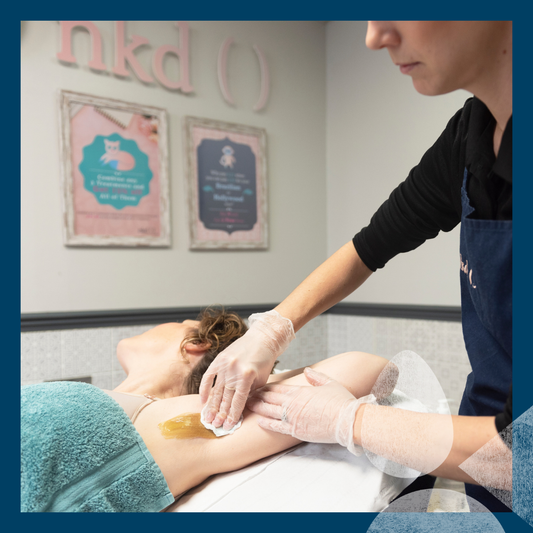
- Ensuring that you care for your skin properly and carefully after all forms of hair removal, when your hair follicles and pores may be open/more prone to damage.
How to Treat Folliculitis?
Treatment for folliculitis depends on the cause and severity.
Mild cases often resolve themselves within two weeks and can be managed with over-the-counter remedies and products – including moisturisers, washes and creams. Products containing ingredients which are naturally anti-bacterial, antiseptic and/or anti-microbial are typically recommended. Such ingredients include tea tree oil, benzoin and aloe vera.
For recurrent or severe cases, it's advisable to seek medical help. A GP or dermatologist may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics, antifungal medications, or antiviral drugs, depending on the infective agent. In some instances, procedures like laser hair removal may be considered to prevent recurrent folliculitis by destroying the hair follicles and reducing overall hair density.
Summary
Folliculitis, a common but often misunderstood skin condition, arises from inflamed and/or infected hair follicles. It's usually caused by damage to these follicles, allowing bacteria, viruses, or fungi to invade. While it can cause discomfort and aesthetic concerns, understanding the condition is the first step towards managing it effectively.
Prevention and avoidance strategies revolve around maintaining good skin health and personal hygiene. And while many cases resolve without medical intervention, persistent or severe folliculitis warrants a visit to a doctor or skincare specialist.
If you do have folliculitis, it’s important to try and resist the urge to scratch or pick at the affected areas to prevent the spread of infection and potential scarring.